Explain API testing with an example
API testing, or application programming interface testing, is a type of software testing that focuses on the testing of individual API methods and the interactions between different APIs. This type of testing is typically performed at the integration level, after unit testing is completed, and before user interface testing begins. It is used to validate that the API behaves correctly and that it meets the requirements of the system.
API testing can be performed manually or using automated testing
tools. Some common tasks that are performed during API testing include:
·
Testing the functionality of the API to ensure it behaves as
expected
·
Verifying that the API returns the correct response for
different input valuesChecking for error handling and validation of input
Testing for security vulnerabilities
·
Checking for performance and scalability of the API
·
API testing is important because it ensures that the different
components of a system can communicate with each other correctly and that the
system can handle a large volume of requests.
It’s also used to ensure that the API is compatible with
different platforms and operating systems, and can be integrated with other
systems and applications.
API Testing : As we know API
stands for Application Programming Interface which acts as an intermediate of
communication between two applications. Due to this intermediary role of API
(Application Programming Interface) two applications talk to each other and
performs the required actions efficiently. API contains a set of rules and
guidelines based on which the applications are developed. So in simple we can
say an API acts as an interface between two software applications so that two
software applications can communicate with each other.
API (Application
Programming Interface) testing is a type of software testing that focuses on
the functionality, reliability, and performance of application programming
interfaces (APIs). APIs act as a bridge between different software systems,
allowing them to communicate and exchange data with each other.
API testing is important because it helps ensure that the different
systems that make up an application are working together correctly and that the
data being exchanged is accurate and secure. It is also important because it
helps identify and fix issues before the application is deployed to production.
API testing typically includes the following steps:
·
Reviewing the API documentation to understand the functionality
and expected inputs and outputs
·
Writing test cases that exercise the different functionality of
the API
·
Executing the test cases and comparing the expected results with
the actual results
·
Analyzing the results and identifying any issues that need to be
fixed
There are several types of API testing, including:
·
Functional testing: Testing the functionality of the API to
ensure it behaves as expected
·
Security testing: Testing the security of the API to ensure it
is protected against common vulnerabilities
·
Performance testing: Testing the performance of the API to
ensure it can handle the expected load
·
Interoperability testing: Testing the compatibility of the API
with other systems
·
Usability testing: Testing the usability of the API for
developers
·
Tools such as Postman, SoapUI, and Runscope can be used to
automate and simplify the process of API testing.
API Testing
refers to test the APIs which are used in the application just to validate that
the APIs are working fine. When a system has a collection of APIs, these needs
to be tested to know that the system is working perfectly or not. Mostly we can
say that API testing confirms system’s performance, reliability, security and
functionality.
Below list represents some of
the tools which are used for API Testing :
·
Postman
·
Katalon Studio
·
Soap UI
·
Parasoft
·
REST assured
·
Tricentis Tosca
·
Ping API
·
Assertible
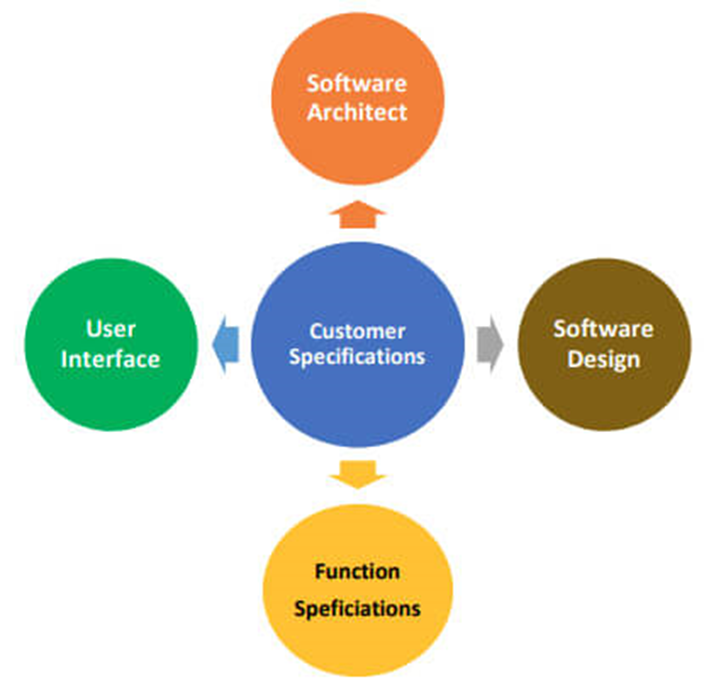
GUI testing is different from the API testing as GUI testing is present at Presentation layer where the API testing is present at Business layer. If we will take an example of a typical app then API is the middle layer in between UI layer and Data base layer and due to this API communication and data exchange between the applications occur. The below figure represents the layer at which API testing is performed
image : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/api-testing-in-software
API
testing Types : There are multiple types of testing which
are most often used as form of API testing which means during multiple types of
testing simultaneously API can be tested. So below list represents the types of
API testing i.e.
1.
Unit testing
2.
Integration Testing
3.
End to End Testing
4.
Performance Testing
5.
Functional Testing
6.
Security Testing
7.
Load Testing
8.
Penetration testing
9.
Reliability Testing
10.
Fuzz Testing
What exactly we check during
API testing :
·
Data accuracy.
·
Response time.
·
Duplicate or missing functionality.
·
Authorization checks.
·
Multithreaded issues.
·
Security and performance issues.
·
Error codes if API returns.
·
Reliability issues.
Benefits of API Testing :
Like we get a lot of advantages by using APIs in
application, similarly by performing API testing we achieve a lot of things
towards the success of the developed application. Below are some of the
benefits i.e.
·
Earlier validation of correctness in response and data.
·
Earlier test maintenance.
·
Better speed and coverage of testing.
·
GUI independent testing.
·
Reduced testing cost.
·
Language independent test.
·
Helpful in testing core functionality.
·
API testing has several benefits that make it an important
aspect of software testing:
·
Improved functionality: API testing helps ensure that the
functionality of the API is working as expected and that the data being
exchanged is accurate and complete.
·
Increased security: API testing helps identify and fix security
vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. This helps
ensure that the API is protected against common threats and that sensitive data
is secure.
·
Improved performance: API testing helps identify and fix
performance bottlenecks, such as slow response times or high error rates. This
helps ensure that the API can handle the expected load and that users have a
positive experience when using it.
·
Better integration: API testing helps ensure that the different
systems that make up an application are working together correctly and that the
data being exchanged is accurate and secure.
·
Reduced risk: By identifying and fixing issues before the
application is deployed to production, API testing helps reduce the risk of
system failure or poor performance in production.
·
Cost-effective: API testing is more cost-effective than fixing
problems that occur in production. It is much cheaper to identify and fix
issues during the testing phase than after deployment.
·
Improved developer experience: By making sure that the API is
easy to use, well-documented, and provides useful error messages, API testing
helps improve the developer experience and encourage adoption.
·
Greater flexibility: API testing allows teams to test the application
without a user interface, which can be useful when testing microservices or
when the user interface is not yet developed.
DISADVANTAGES OF API TESTING :
API testing can have some disadvantages, including:
·
Complexity: API testing can be complex, especially when testing
multiple APIs or when testing APIs that are integrated with other systems.
·
Limited Visibility: Since API testing is performed at the
integration level, it can be difficult to see how the API is interacting with
other components of the system. This can make it difficult to identify and
troubleshoot issues.
·
Security: APIs can introduce security vulnerabilities if they
are not properly tested and secured. This can be a significant concern for
organizations that handle sensitive data.
·
Difficulty in testing non-functional requirements:
Non-functional requirements such as performance, scalability and security are
difficult to test with functional testing
·
Time consuming: The time required to develop and execute test
scripts for APIs can be longer than other types of testing.
·
Limited documentation: Limited or poor documentation of the API
can make it difficult for testers to understand how the API should behave.
·
Limited test coverage: It is difficult to test all possible
scenarios and edge cases with API testing.
·
Cost: Automated API testing tools can be expensive and require a
significant investment.
Reference:


Comments
Post a Comment